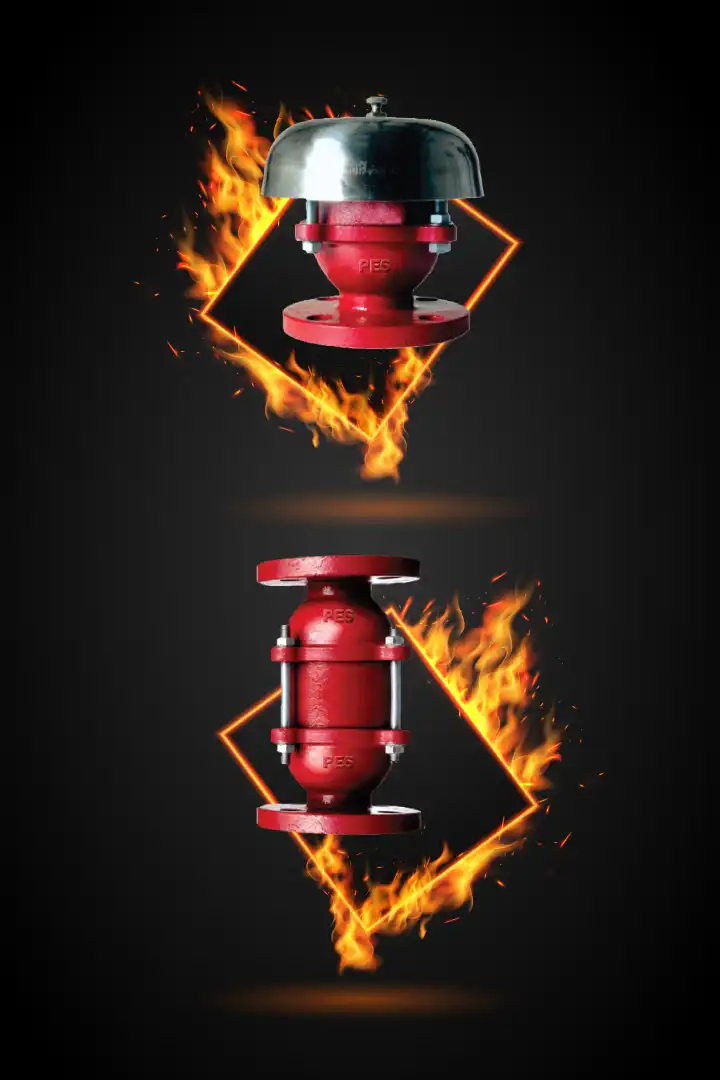
In industries where flammable gases, vapors, or liquids are present, safety is paramount. Flame arrestors serve as critical safety devices, preventing the propagation of flames and mitigating the risk of fires and explosions. This article delves into the significance, working principles, types, applications, and advantages of flame arrestors.
Introduction to Flame Arrestors
Flame arrestors are passive safety devices engineered to halt the spread of flames in potentially explosive atmospheres. They operate by cooling hot gases and absorbing heat, effectively containing deflagrations and detonations.
Why Flame Arrestors are Essential
Preventing Explosions: By hindering flame propagation, flame arrestors prevent catastrophic explosions in industrial settings.
Reducing Fire Risk: They mitigate the risk of fires by preventing sparks or flames from igniting flammable substances.
Enhancing Safety: Flame arrestors ensure a safer working environment for personnel and equipment.
Low Maintenance: These devices require minimal upkeep, contributing to cost savings and operational efficiency.
Cost-effectiveness: Flame arrestors offer a cost-effective solution for safeguarding industrial operations.
Regulatory Compliance: Compliance with safety regulations, such as OSHA and NFPA, is facilitated by the use of flame arrestors.
Working Principle of Flame Arrestors
Flame arrestors function by impeding the progression of flames through the following mechanisms:
Cooling Hot Gases: Metal plates or mesh screens within the device absorb heat from flames, cooling the gases and halting propagation.
Quenching Element: Some flame arrestors utilize a quenching element to release a mist of water or other fluids, further cooling gases and disrupting flame fronts.
Types of Flame Arrestors
Deflagration Arrestors: Designed to prevent flames from reaching the ignition source by cooling hot gases.
Detonation Arrestors: Employ a complex design to dissipate the energy of detonations, which are more severe than deflagrations.
In-line Flame Arrestors: Installed within process lines to prevent flame propagation between vessels.
End-of-Line Flame Arrestors: Positioned at the end of process or vent lines to prevent flames from escaping into the atmosphere.
Pressure/Vacuum Relief Flame Arrestors: Relieve pressure or vacuum in vessels while preventing flame propagation.
Spark Arrestors: Traps and cools hot particles to prevent sparks from causing fires or explosions in outdoor equipment.
Applications of Flame Arrestors
Flame arrestors find extensive usage across various industrial sectors:
Oil and Gas Industry: Used in pipelines, tanks, and equipment to prevent explosions and fires.
Chemical Industry: Employed in processing plants to mitigate the spread of flames in reactors and distillation columns.
Pharmaceutical Industry: Ensures safety in equipment handling flammable solvents.
Refineries: Prevents explosions and fires in storage tanks and pipelines.
Power Plants: Essential for safety in fuel storage and handling systems.
Mining Industry: Safeguards equipment handling flammable substances like diesel fuel.
Aerospace Industry: Crucial for preventing fires and explosions in fuel systems.
In summary, flame arrestors play a vital role in maintaining safety and preventing disasters in industrial environments where the presence of flammable materials poses inherent risks. Understanding their operation, types, and applications is crucial for ensuring the protection of personnel, equipment, and facilities.